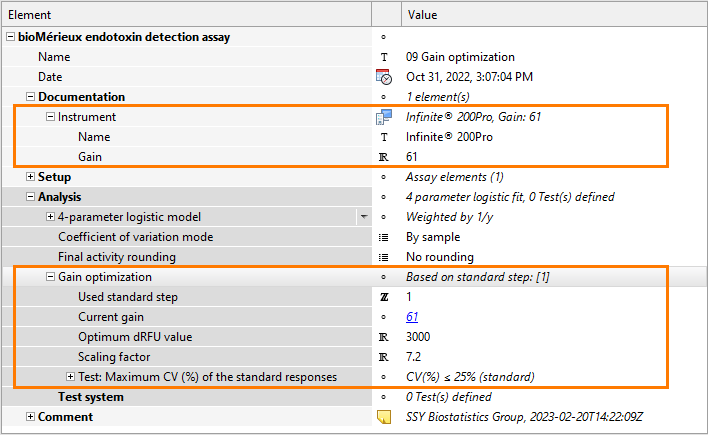
Gain optimization
The gain of a plate reader reflects its dynamic range, indicating the level at which reasonable measurements can still be carried out. bioMérieux endotoxin detection assay documents let you define a gain optimization routine, therefore providing the data you need to adjust the signal amplification to maximize dynamic range and ensure the results remain within the instrument's detection limits.
The dynamic range of a plate reader is the ratio between the brightest and darkest light intensity. By optimizing the gain, you can avoid over-saturating the detector with signals that are too strong or failing to detect signals that are too weak. This ensures that both high and low concentration samples are measured accurately, contributing to reliable endotoxin quantification.
Instrument gain
Use the Creatable elements pane to add an Instrument element, and define the name and gain of your instrument.
Gain optimization
Use the Creatable elements pane to add a Gain optimization element, and define the optimization parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Used standard step |
Select the dose step of the Standard sample to be used as reference for determining the optimum instrument gain. Commonly, the dose step of the Standard sample with a nominal concentration of about 0.5 EU/ml is used for determining the optimum instrument gain. |
|
Current gain |
Select the gain used for the measurement. This is the gain you entered for the instrument in the Documentation section of this assay document. |
| Optimum dRFU value |
Enter the value expected to be measured for the concentration of the selected dose step. The value to use depends on the analytical configuration and the test kit and instrument used for the assay. |
|
Scaling factor |
The scaling factor is used to determine the optimum instrument gain, taking into account the Optimum dRFU value and the average dRFU of the dose step. The value to use depends on the analytical configuration and the test kit and instrument used for the assay. |
