Cylinder plate assays (USP <81>)
Use Cylinder plate assay (USP <81>) documents to determine the potency of antibiotics according to the cylinder-plate method described in USP <81>. PLA 3.0 uses a linear regression model to fit the standard curve. This method allows you to correct for plate-to-plate variation.
To determine absolute potencies, PLA 3.0 interpolates the response values of the test samples on the standard curve. It calculates relative potencies based on the reference step of the standard.
About this document type
This document type lets you organize observation data, calculate potencies, and define statistical tests for individual microbial assays. It lets you closely follow the guidelines laid out in USP <81>, but also provides considerable flexibility. Moreover, it lets you document supplemental information on the setup of experiments.
Document structure
Each Cylinder plate assay (USP <81>) document has three sections, that is, Setup, Analysis, and Documentation, plus one or more optional Comment sections.
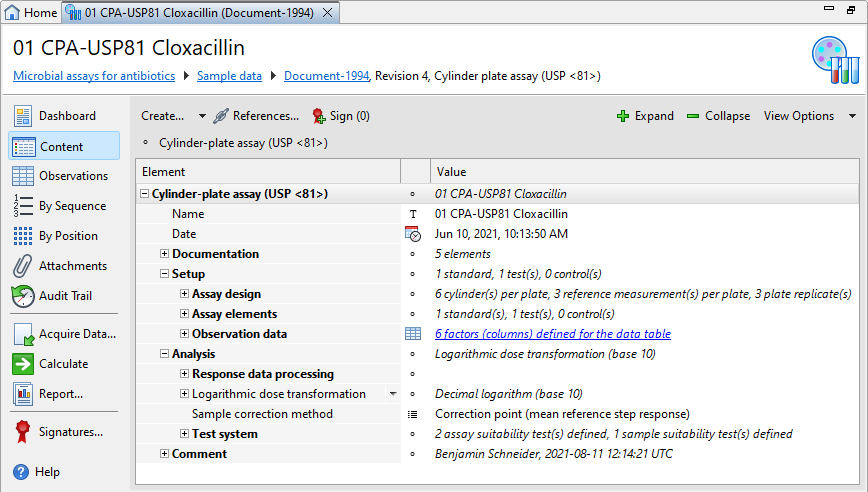
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
|
Documentation |
Provide supplemental information on the setup of experiments that is needed for documentary purposes, but is not required to calculate potencies or organize observation data. |
|
Setup |
For details on the available settings, see the Assay setup topic. |
|
Analysis |
For details on the available settings, see the Assay analysis and Test system topics. |
|
Comment |
Add extra information to your assay. The PDF reports display the comments you add on the first page. You can use a simplified Wiki notation for the text. For details on the Wiki notation, see the Simplified Wiki notation topic. |
